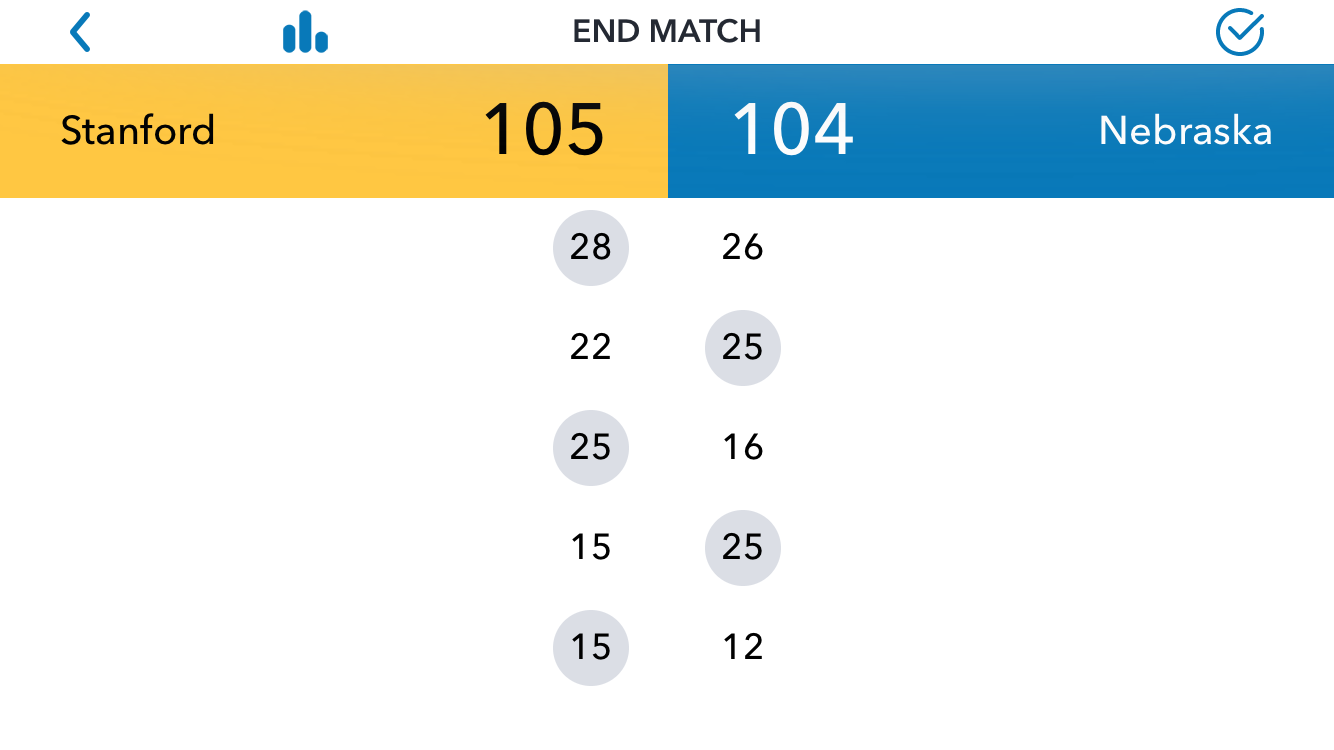
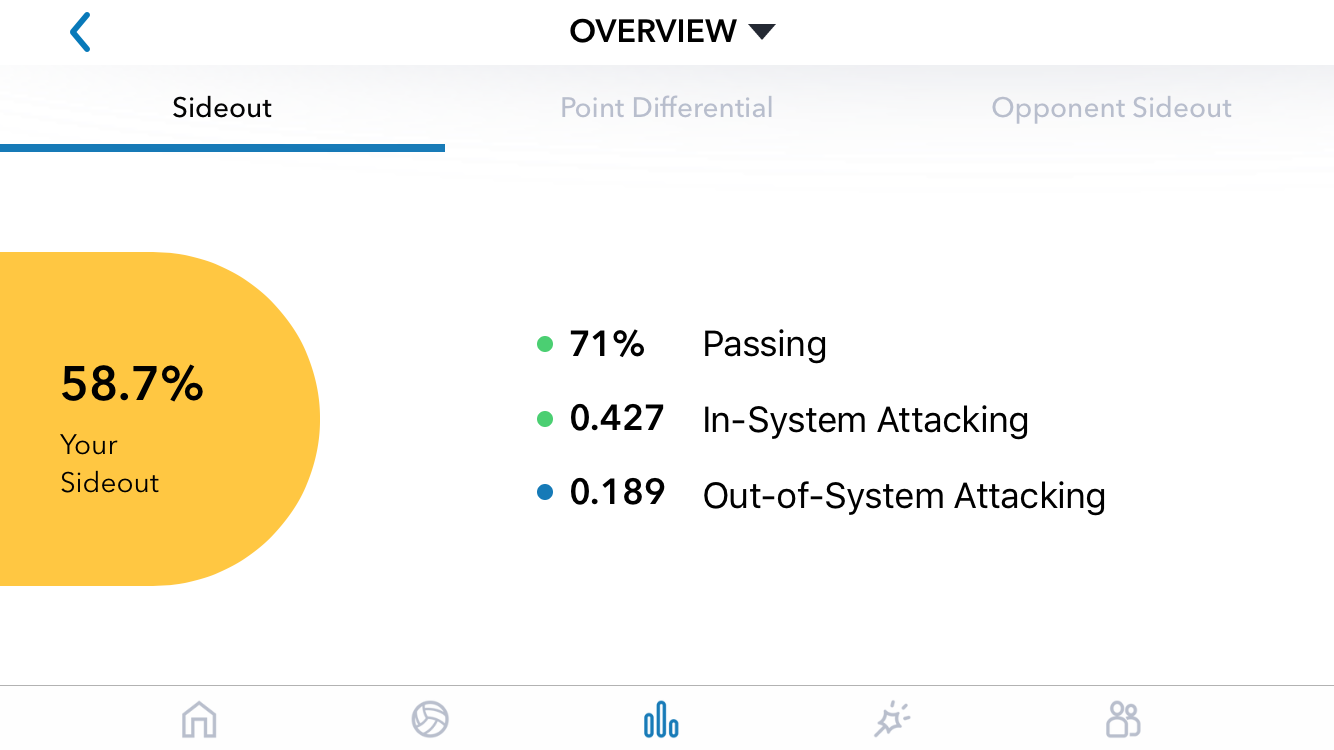
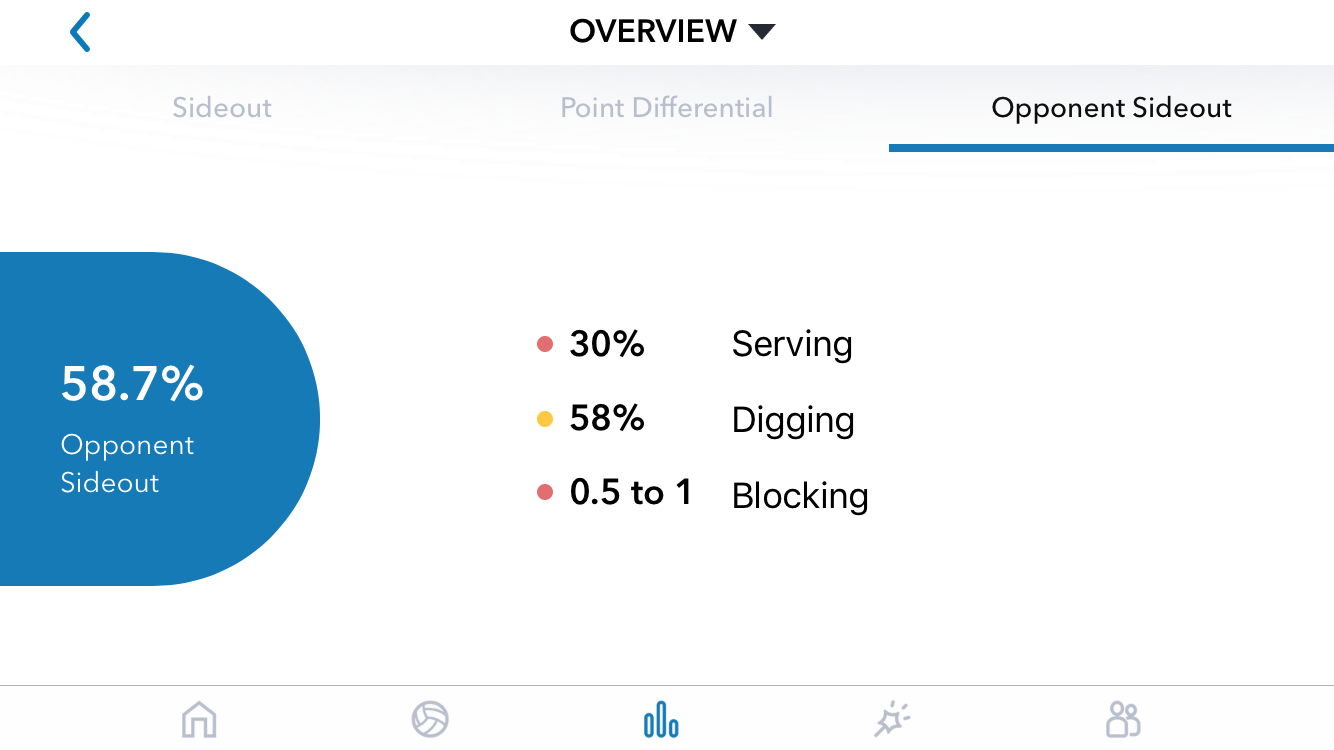
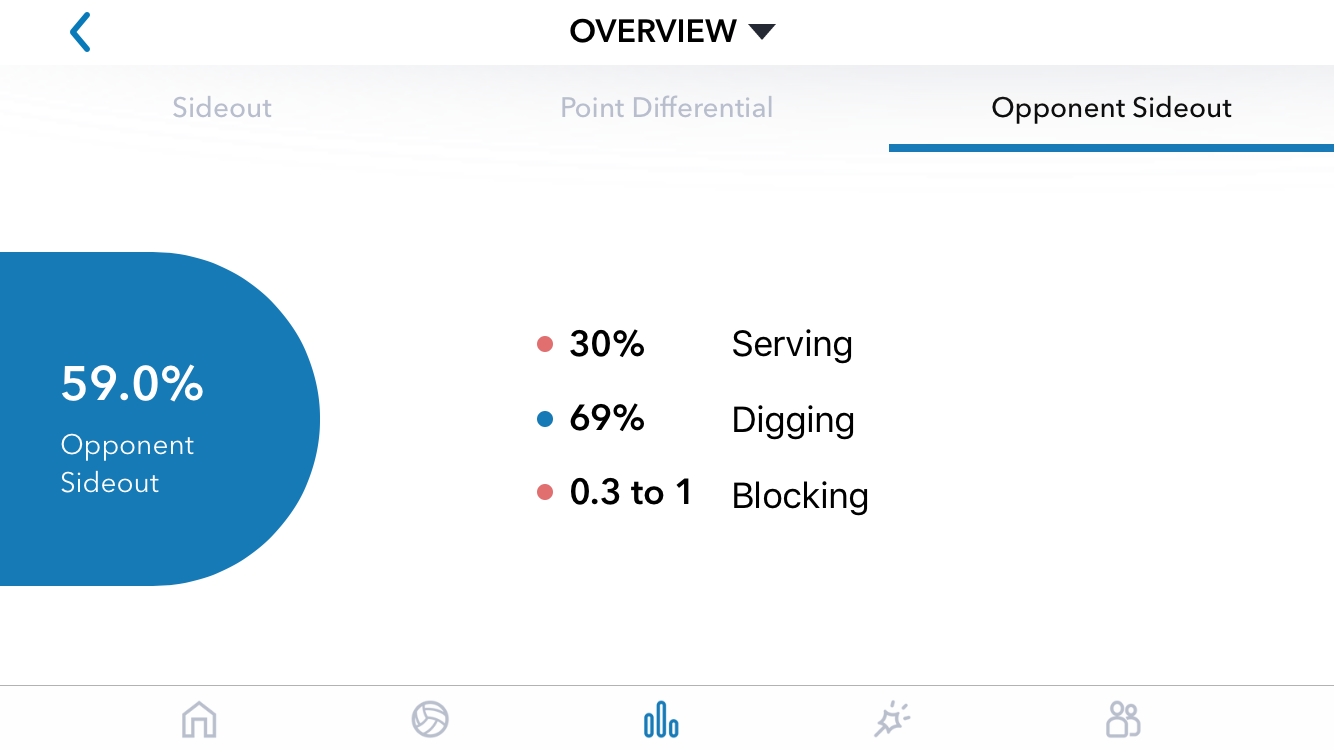
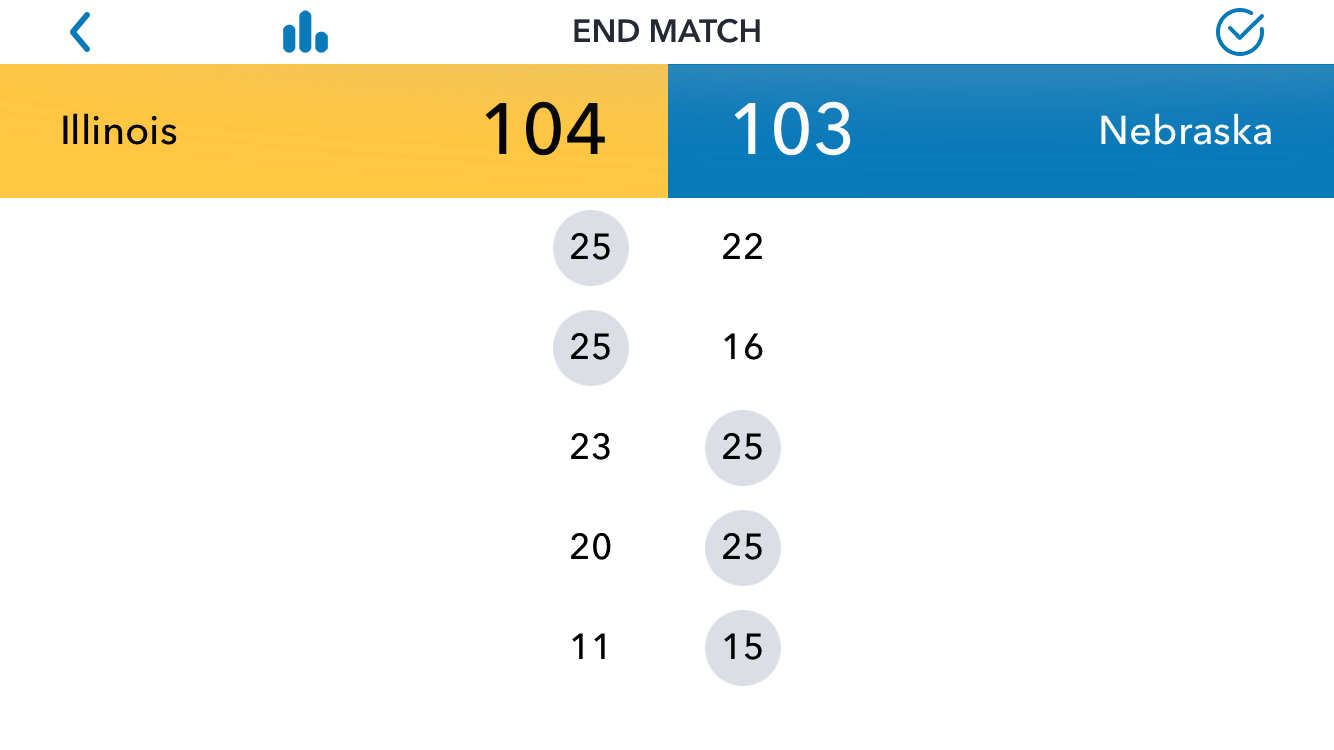
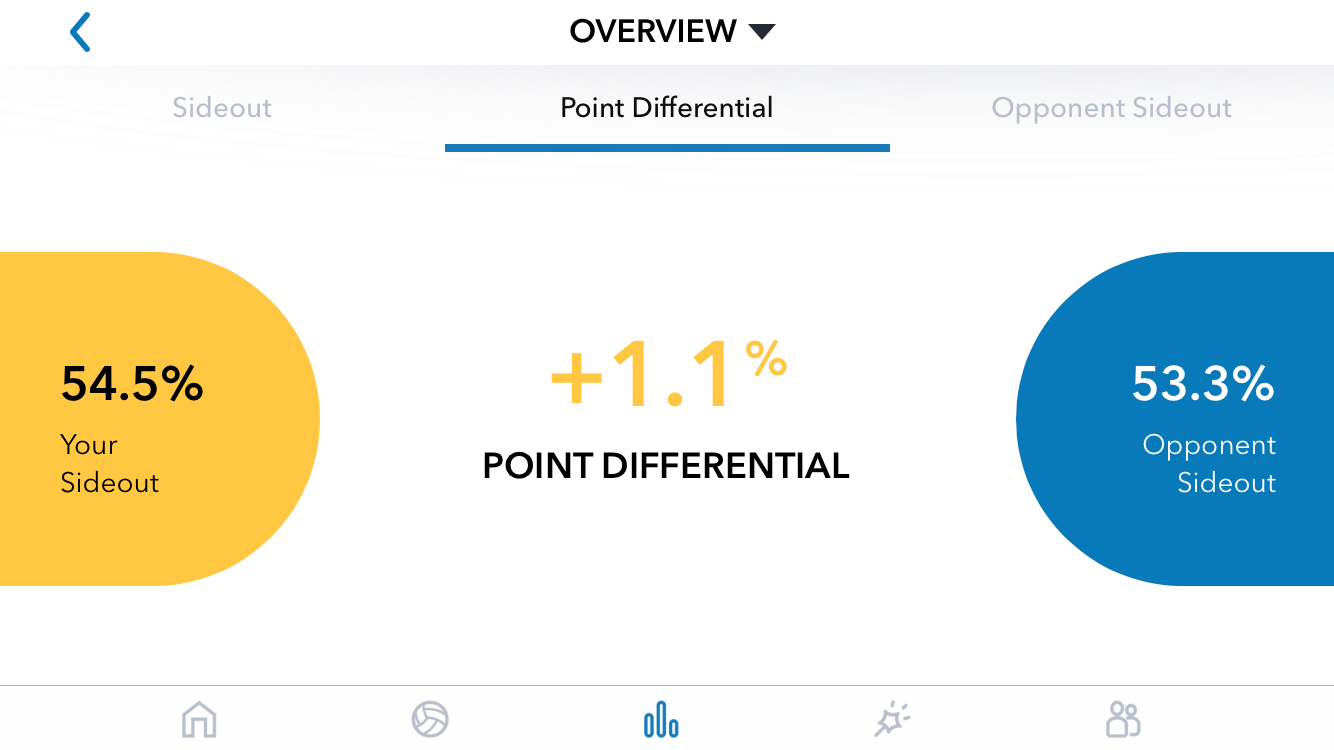
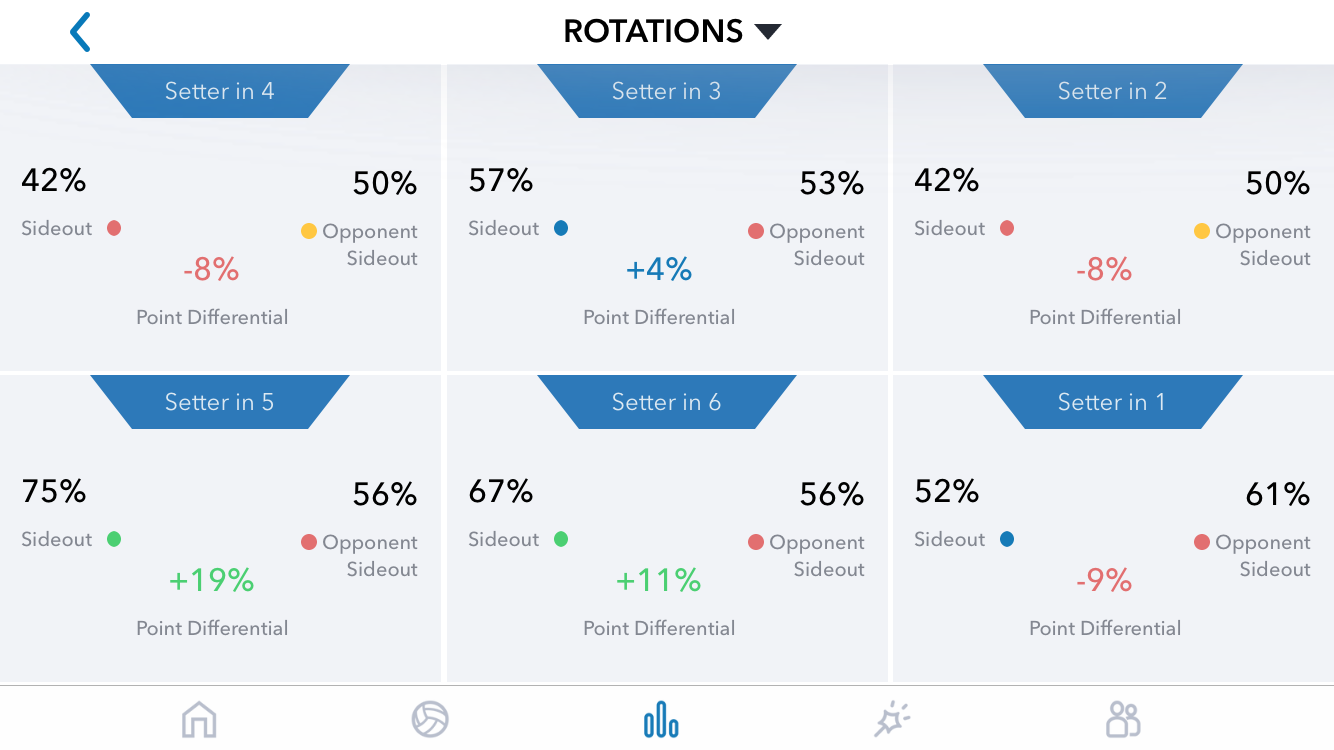
In Part 1 of this article, I shared a question from a Workshop participant:
I would be curious to hear your opinions on what you think the most important things would be for a young assistant coach to have in their toolbox or qualities that they should have. I’m getting ready to transition from my graduate assistant role into (hopefully) a full time assistant coach role after the 2020 season and looking for almost some direction.
I shared some thoughts on the statement, “it’s not what you know, it’s who you know,” as well as two skills to have in the toolbox. I have another to share today.
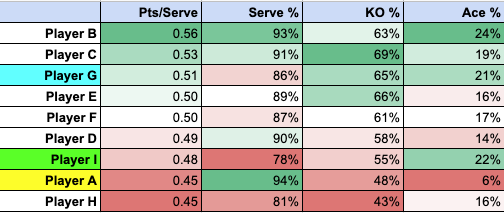
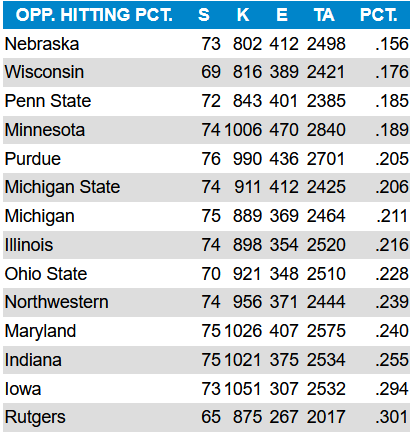
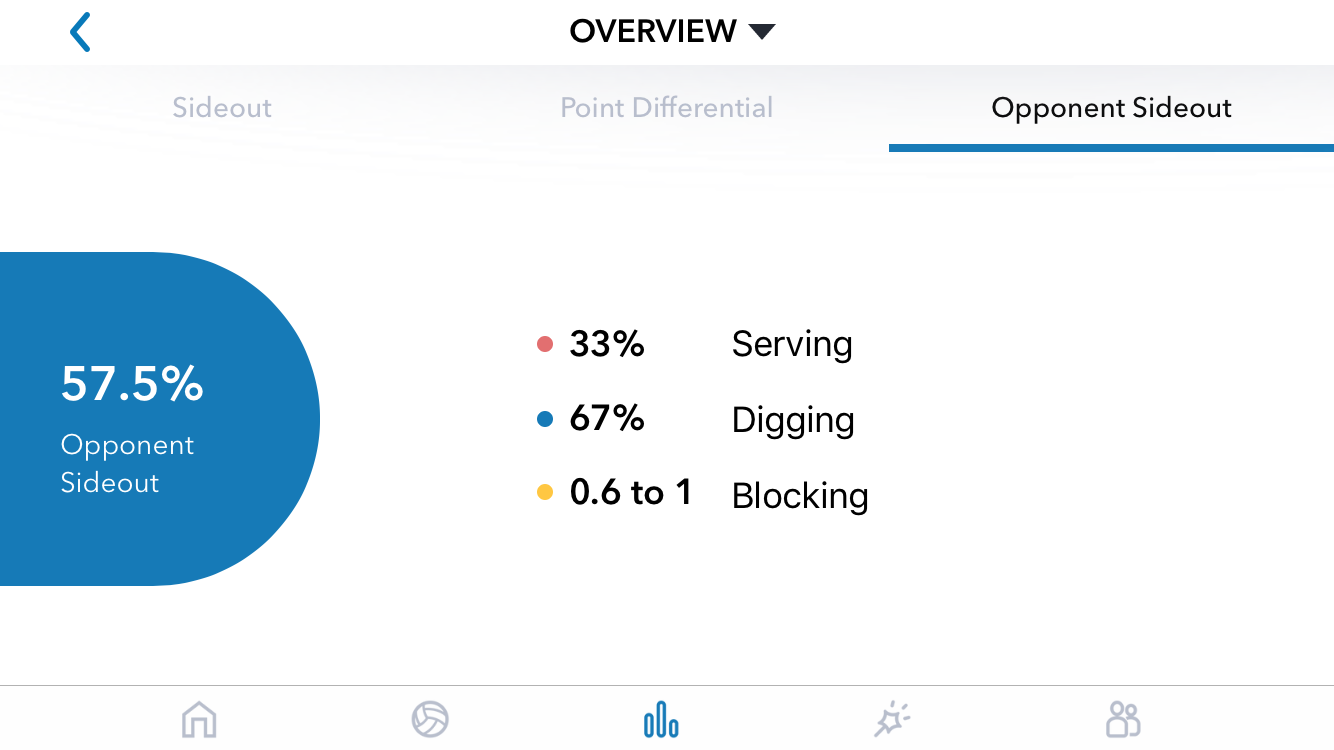
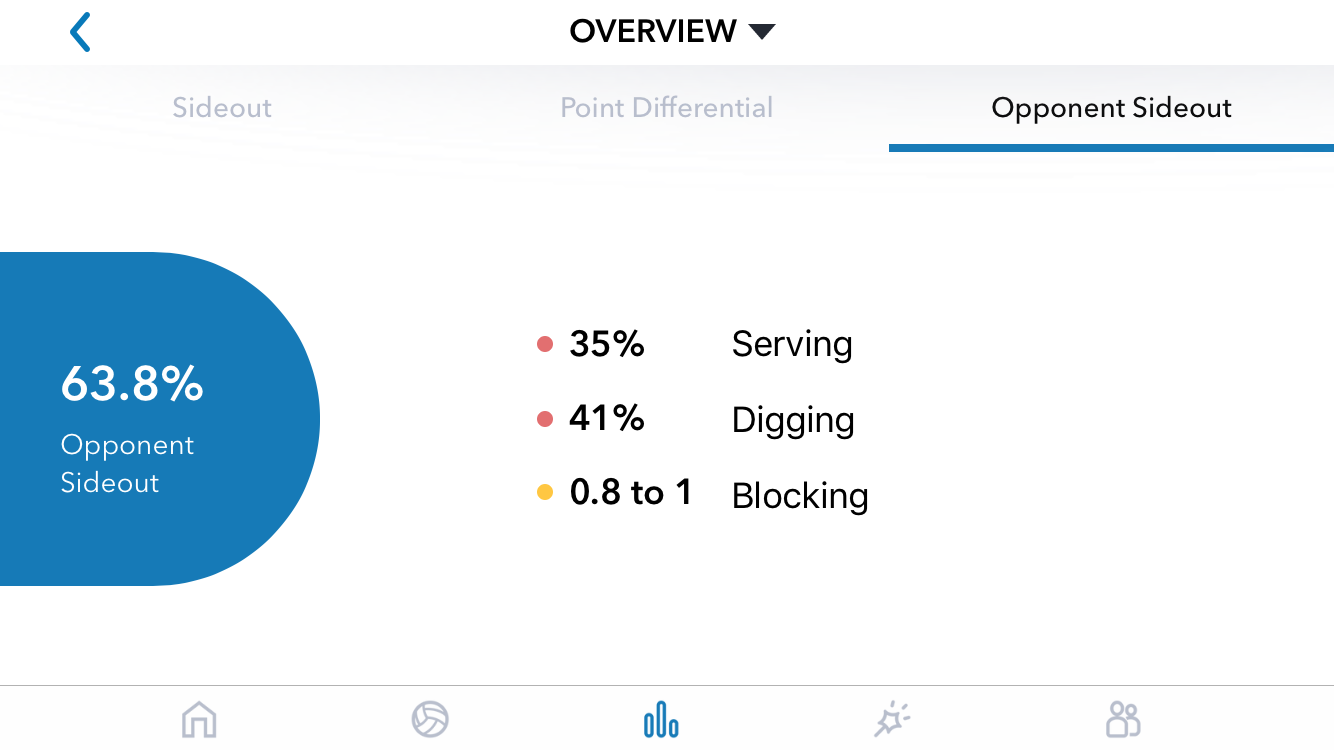
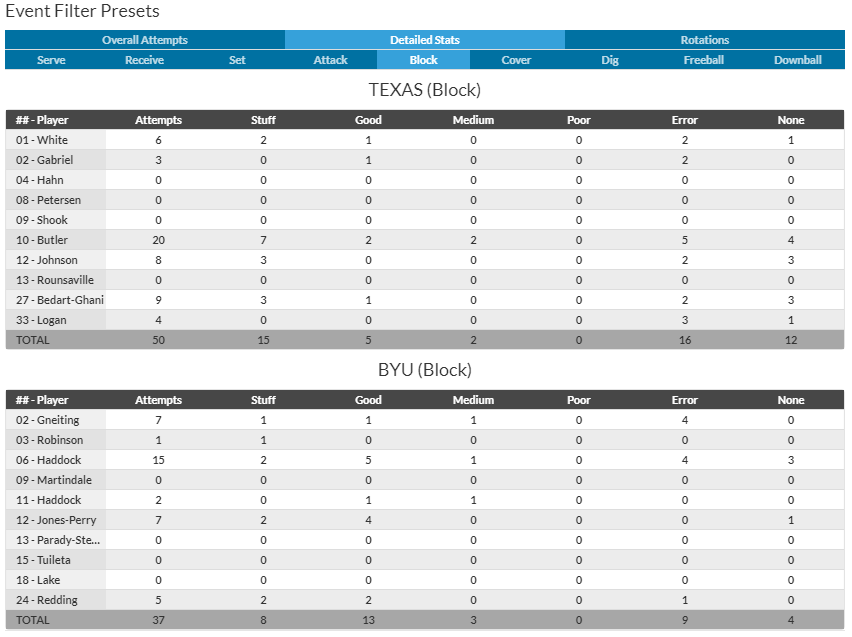
DataVolley, Analytics, Video
Learn DataVolley. If you want to be involved in high-level volleyball, and you don’t have a high-level playing background, this is one of the best ways to make yourself valuable. I played Division 3 volleyball and I’ve been part of an Olympic staff. DataVolley and analytics was the way I added value that my playing background didn’t bring.
It also makes you a better coach.
In 2002, all of the best poker players in the world were old guys with names like Lakewood Louie, Amarillo Slim, and Bones Berland. Actually, those guys were bigger in the 70s and 80s, but they have cooler names than Phil Ivey and Johnny Chan. Let’s move on. The point is, was that high-level poker had high-barriers to entry (like… money) and poker, like many things in life, takes practice to get good at.
Enter online poker. In 2003, the World Series of Poker Main Event was won by a guy named (I’m not making this up) Chris Moneymaker. Chris made a cool $2.5 Million dollars for that, but he made online poker companies a LOT more, because he was the first WSOP winner to qualify through an online tournament, rather than in-person, casino-hosted tournaments.
Within a few years, online poker’s takeover was complete. Almost all of the top players were playing online, and soon many of the top players were under 30 or even under 25. Why? Because online poker allows you to play FAR more hands than in-person poker. First of all, you don’t have to physically drive to the casino, park, leave the table to go eat, etc. Computers shuffle and deal way faster than human dealers. And many online players would play in several virtual tables at once. You can imagine the difference in learning curve when you go from playing 25 hands/hour in a live game to playing 4 simultaneous tables that are playing at a rate of 75 hands/hour. These players were literally 10xing their progress.
I think you can see the connection to DataVolley.
I grew up in Delaware. I played Division 3 volleyball. I saw a few Olympic Volleyball matches on television. I didn’t even know there was a World Championship or what a Grand Prix was. The best volleyball I could reliably see in-person was when somebody from the Pac 12 or Big 10 would travel to play the University of Delaware for strategic RPI reasons.
If I was relying on being able to be involved in-person in high-level volleyball… I’d still be waiting.
In February of 2012, I had seen close to 0 elite level volleyball. By June of 2012 (after a few months into an accidental volunteer position with the USA National Team… more on that another time) I had maybe 200 hours of live National Team practice under my belt…. and at least double that in elite level volleyball studied on video.
Every day I was going home and studying hours of video. It was to practice and learn coding, but I discovered I was also learning volleyball. The great thing about video is that you can rewind it. Over and over again. You can keep watching a play until you really understand it. You can watch it through and focus on the setter, and then watch it again and focus on the attacker, and then watch it again and focus on the blockers. You can really understand how each person contributes to the play.
The other thing about DataVolley and coding is that the nature of grading each play means that you start compiling this mental image of “this is what perfect passes look like… this is what bad passes look like.” It kind of tunes you in to that on a subconscious level.
The video end also gave me a lot of confidence interacting with elite players. I knew what I saw on video. I knew when I was scouting an opponent that I could watch them until I was 100% confident in what I was seeing. If I was just relying on experience and intuition, how could I be confident in what I was saying? But the video allows you to watch it until you’re sure. So I did!
There’s just too many benefits to being good with video to ignore it. Get out there and start studying it. And if you want to learn DataVolley even faster, try checking out this manual written by two guys who spent a lot of time with the program. :)